
Overcoming Migration Challenges
With the current technology transformation scenario, modern enterprises understand the need to migrate data from legacy systems. Thus, legacy system migration is a significant process to migrate information from old legacy structures to modern platforms. Let’s get into the in-depth and explore the challenges of data migration and unravel the exponents and practical insights for successful transitions. With the constant changes in data platforms and their structure, the usage of legacy systems has become a bottleneck for modern enterprises' growth. These traditional systems have intricacies of limited scalability, major security liabilities, and major maintenance difficulties, along with unsuitability with fast-changing technologies. The process includes transferring critical business data from older structures to newer ones with efficient features.Considered Best Practices Associated with Data Migration
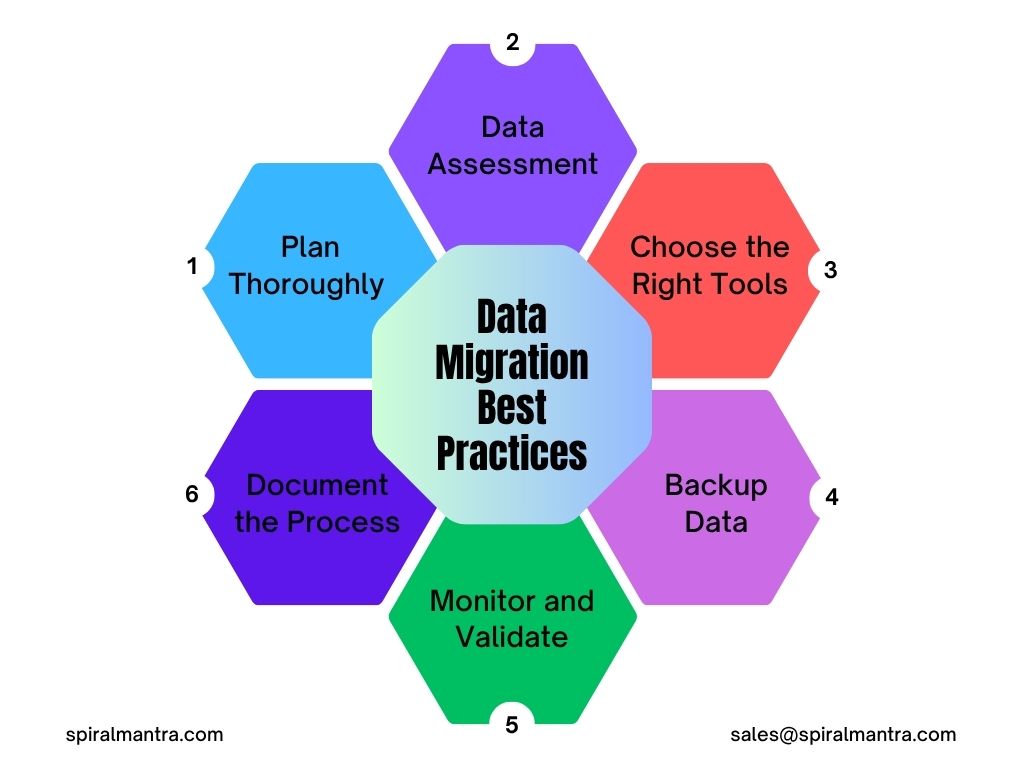 The successful cycle of data migration adherence follows proven methodologies to minimize security risks while maximizing efficiency. Any migration project foundation begins with an extensive assessment in the discovery phase; thus, businesses should catalog the local and existing structure of information with its dependencies on current datasets before finalizing transfer activities.
Another best practice facilitates in-depth documentation of the entire process, comprising final decisions, major challenges faced, and procedure details. Maintaining detailed records of business logic, major transformation rule summaries, and data lineage helps to understand what important changes are needed to adapt while transferring information to the new system. Therefore, this document becomes invaluable to understanding the core of business from testing to post-migration.
The quality enhancement of your current business data must be viewed as an upgraded opportunity to cleanse old existing datasets from the CI CD pipeline and eliminate duplicate forms with standardized formats. Also, it helps to implement improved governance practices by leveraging data quality migration initiatives associated with long-term benefits as a whole for the systems.
The successful cycle of data migration adherence follows proven methodologies to minimize security risks while maximizing efficiency. Any migration project foundation begins with an extensive assessment in the discovery phase; thus, businesses should catalog the local and existing structure of information with its dependencies on current datasets before finalizing transfer activities.
Another best practice facilitates in-depth documentation of the entire process, comprising final decisions, major challenges faced, and procedure details. Maintaining detailed records of business logic, major transformation rule summaries, and data lineage helps to understand what important changes are needed to adapt while transferring information to the new system. Therefore, this document becomes invaluable to understanding the core of business from testing to post-migration.
The quality enhancement of your current business data must be viewed as an upgraded opportunity to cleanse old existing datasets from the CI CD pipeline and eliminate duplicate forms with standardized formats. Also, it helps to implement improved governance practices by leveraging data quality migration initiatives associated with long-term benefits as a whole for the systems.
Data Migration: Step-By-Step Process Guide
Initiating the process associated with fulfilling major key steps of data migration, as it follows a structured approach in all major distinct phases, including planning and execution. The initiating phase involves proper planning of stakeholder alignment, timeline decision-making, resource distribution, and allocation with risk assessment. The phase is ideal for identifying the loopholes in information structure, defining the next criteria for success, and establishing protocols for communication and security essentials. The second phase is determined by the current IT architecture assessment, in which the technical teams will be involved in analyzing existing systems, identifying integration points, and evaluating major quality issues. The associated phase often discloses all the hidden complexities that work on the ongoing migration strategies. The designing and architecture part is focused on configuring data transformation rules along with identifying integration points that can be useful to evaluate major quality-related issues. This associated phase is determined to disclose all relevant complexities encountered by the enterprise; thus, it is helpful to establish the technical blueprint that can be helpful to understand subsequent implementation activities. The fourth phase is derived to be the implementation phase, which encompasses the extraction of actual data, transformation, and loading at last. This stage requires comprehensive coordination among the technical teams and business users. Enterprises can execute parallel testing by implementing validated system performance, business processes, and information accuracy functionality. Upon completing the migration, post-migration support takes place to assess all the aspects of data migration from legacy systems to modern architecture. The procedure is ideal to identify all the emerging issues and quickly address them to fix them accordingly with the new information architecture capabilities.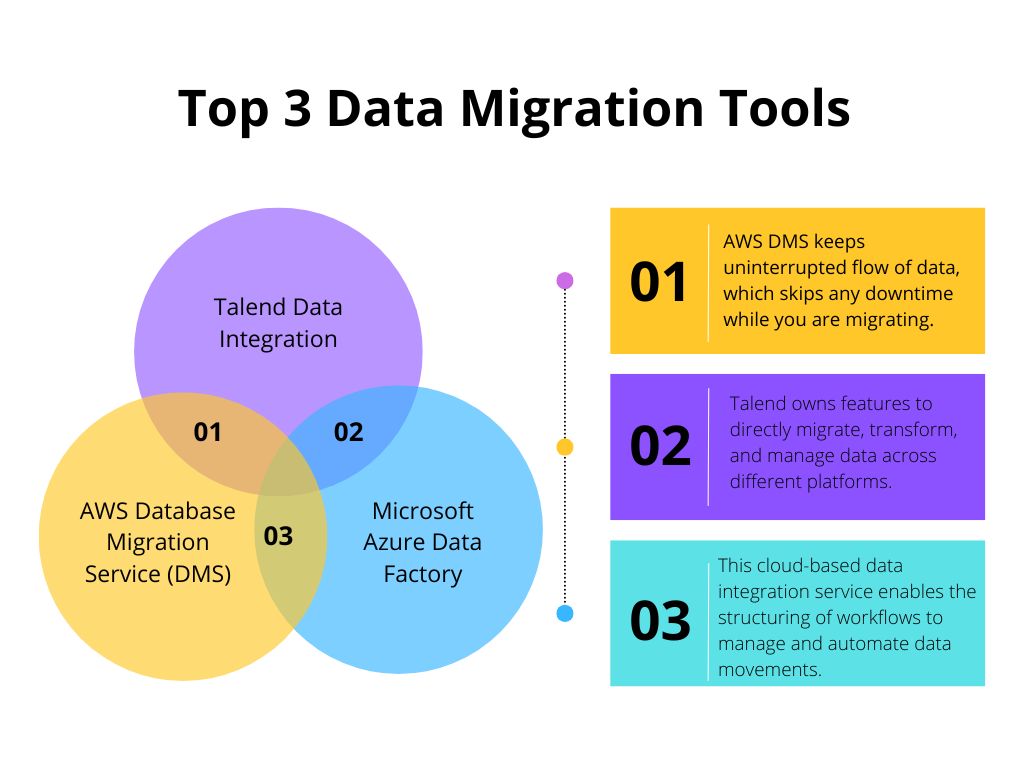
Adaptable Solutions Reducing the Data Migration Risks
Multiple factors should be adopted by enterprises to reduce migration risks. The first one is associated with adapting risk mitigation strategies by adhesively addressing testing protocols, which include performance testing, integration testing, and unit testing, along with user acceptance testing. Automated testing tools can be utilized to resolve complex transformation scenarios by validating large datasets to achieve this. Business continuity planning protects against operational disruptions during migration activities. Organizations should develop detailed rollback procedures, maintain parallel system operations where feasible, and establish clear escalation protocols for addressing critical issues. Phased migration approaches can reduce risks by allowing organizations to validate results before proceeding with subsequent data sets. Communication and stakeholder management help minimize organizational risks associated with change resistance and unrealistic expectations. Regular progress updates, transparent issue reporting, and proactive stakeholder engagement contribute to project success and user adoption. Additionally, data security and compliance considerations require major attention during the migration procedure. Therefore, enterprises should ensure that all sensitive information remains secure throughout the transfer process and meets all regulatory requirements, such as encryption protocols, access controls, and security audits, to execute the validation.

